- 146 Posts
- 208 Comments

 1·28 days ago
1·28 days agowhat do you think of my scores? am i improving?

 1·28 days ago
1·28 days agoto see the table please use light mode

 1·28 days ago
1·28 days agoi am strugling with netflow i tried to understand it using gpt, is this info enough?
SNMP vs. NetFlow: Understanding Their Roles in Network Management
Both SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and NetFlow are important for network monitoring and management, but they serve different purposes.
What is SNMP?
SNMP is a protocol used to monitor and manage network devices such as routers, switches, servers, and printers. It allows administrators to collect information about device performance, health, and network activity.
Key Features of SNMPv3 (Latest Version)
- Message Integrity – Ensures data is not altered during transmission.
- Authentication – Confirms that messages come from legitimate devices.
- Encryption – Protects SNMP messages from unauthorized access.
- SNMP Traps – Devices can send alerts (traps) to management systems in case of significant events (e.g., a router failure).
📌 Use Case: SNMP is ideal for device health monitoring, fault detection, and performance tracking.
What is NetFlow?
NetFlow, developed by Cisco, is a protocol used for collecting and analyzing network traffic data. It helps administrators understand the source, destination, volume, and flow paths of traffic.
Key Features of NetFlow
- Traffic Profiling – Helps identify trends in network usage.
- Security Monitoring – Detects anomalies and potential threats.
- Efficient Data Collection – Unlike full packet captures, it stores metadata (IP addresses, ports, protocols, etc.).
- Integration with SIEM Tools – Works with security tools like Splunk, IBM QRadar, and ArcSight to analyze network behavior.
📌 Use Case: NetFlow is great for security monitoring, bandwidth analysis, and anomaly detection.
Comparison: SNMP vs. NetFlow
Feature SNMP NetFlow Purpose Device monitoring & management Traffic analysis & flow monitoring Data Type Device status, CPU, memory, uptime, etc. Network flow metadata (IP, ports, protocols, etc.) Security Focus Authentication & encryption for management data Identifies suspicious network behavior & threats Real-Time Alerts Yes (via SNMP Traps) No (but can detect anomalies over time) Traffic Analysis No Yes Complexity Simple More detailed
When to Use SNMP vs. NetFlow?
- Use SNMP when you need to monitor device health, check CPU/memory usage, and receive alerts on hardware failures.
- Use NetFlow when you need to analyze network traffic, detect security threats, or monitor bandwidth consumption.
💡 In practice, organizations often use both SNMP and NetFlow together for a complete network monitoring solution. 🚀

 31·28 days ago
31·28 days agoyou can see it’s peak around 350 km away
rogain also works, don’t tell me you believe in pfs?
it is the most widespread though
Answer: kind of, as long you keep applying the substance you will regrow all the hair that you have lost and maintain it

 11·1 month ago
11·1 month agowhy are you downvoting me i am right? it’s useless to delete comments

 24·1 month ago
24·1 month ago

 452·1 month ago
452·1 month agoi heard he is getting rehired today

 17·1 month ago
17·1 month ago-
Genocide refers to the deliberate destruction of a group based on its identity, as defined by Raphael Lemkin, who introduced the term after witnessing the horrors of Nazi atrocities. The term was legally recognized in 1946 by the United Nations. Genocide includes actions such as killing, causing harm, and inflicting conditions that destroy a group. Israel’s military actions in Gaza are not aimed at destroying the Palestinian population but targeting Hamas, a terrorist organization. Statements from Israeli officials and military practices reinforce that Israel does not intend to harm innocent civilians in Gaza.
-
Israel’s military response in Gaza is aimed at Hamas, not the Palestinian population, which is not genocide but a defense against a terrorist group that seeks Israel’s destruction. Hamas’s actions represent genocidal intent, targeting Israeli civilians and propagating hatred against Jews. Israel’s actions are consistent with international law, focusing on eliminating Hamas and its military infrastructure in Gaza. The use of significant military force is justified, given Hamas’s attacks on Israel. These actions are not genocide, as they are in direct response to a genocidal attack by Hamas.
-
Israel’s military efforts are designed to minimize harm to Palestinian civilians, with the IDF issuing warnings before strikes and setting up humanitarian corridors. Despite challenges, Israel’s focus is on protecting civilians by evacuating them from battle zones and providing aid. The actions reflect Israel’s desire to protect civilians from harm while addressing the threat posed by Hamas. Claims of genocidal intent are contradicted by Israel’s humanitarian efforts in Gaza. The goal is to remove civilians from harm’s way while dismantling Hamas’s infrastructure.
-
Hamas deliberately places Palestinian civilians in harm’s way to use them as human shields and to manipulate public opinion by inflating civilian casualties. It fires missiles from civilian areas, turning them into legitimate military targets. While Israel aims to avoid civilian harm, it cannot entirely eliminate the risk due to Hamas’s tactics. The responsibility for civilian casualties lies with Hamas, which exacerbates the situation by using civilian sites to shield its operations. Israel’s military actions, while tragic, are legally justified in targeting legitimate military objectives.
-
Claims of genocide by Israel in Gaza are based on misunderstandings and unverified information. The true circumstances surrounding civilian casualties are unclear due to Hamas’s control of Gaza’s health ministry and its influence on casualty reporting. The real causes of civilian deaths, including whether they were caused by Hamas’s actions or Israeli strikes, are often unclear. Claims of genocide are fueled by misinformation, and the real blame for civilian suffering should lie with Hamas. Efforts to end the suffering in Gaza would be better focused on defeating Hamas, ensuring peace for both Palestinians and Israelis.
-

 217·1 month ago
217·1 month agothey started the war and they lost? why should israel make the concession?

 92·1 month ago
92·1 month agothey were allegedly calling for violence against musk

 16·1 month ago
16·1 month ago☮fool

 72·1 month ago
72·1 month agogod is giving us a sign, it’s time to protest
50501

 123·1 month ago
123·1 month agoDonald Trump, please save us, please save us, Donald Trump, if you can hear me…

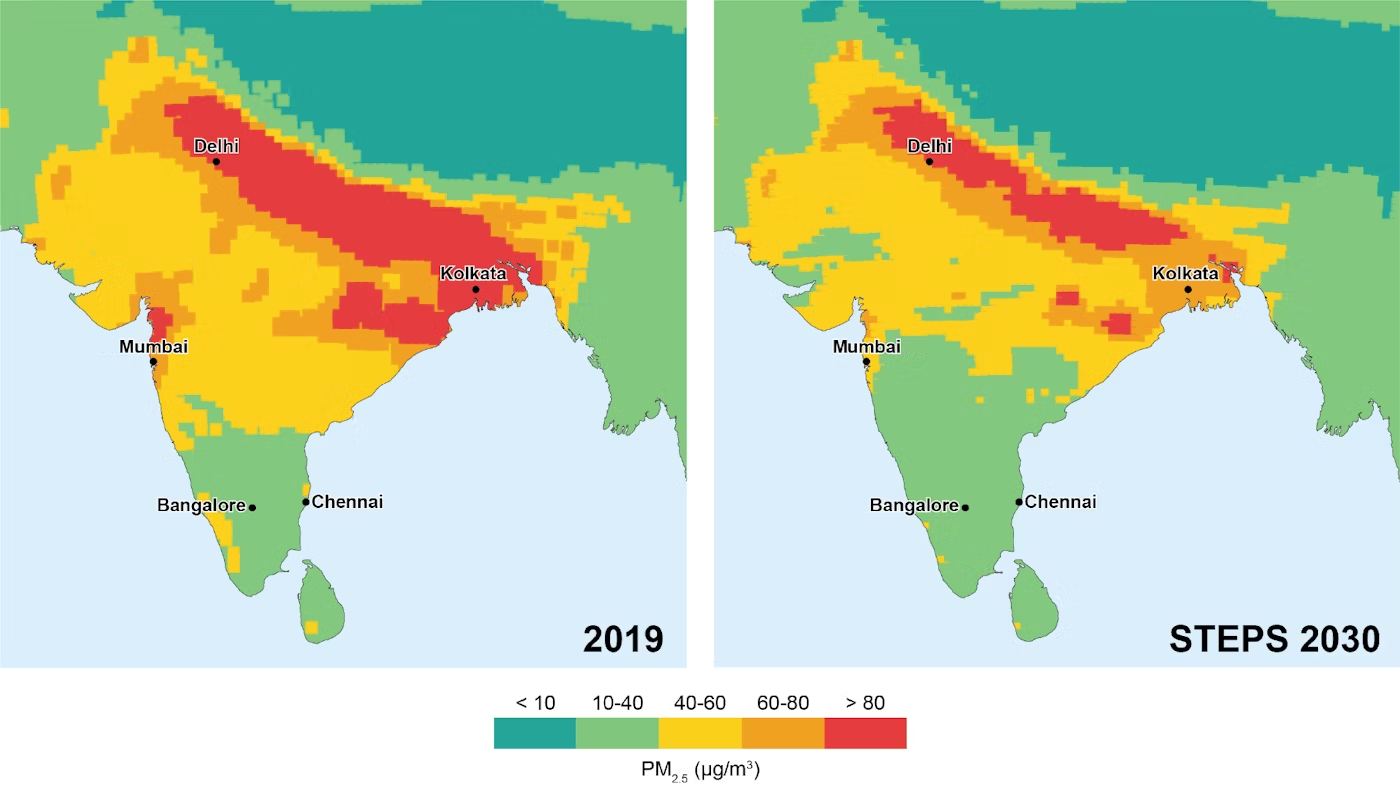
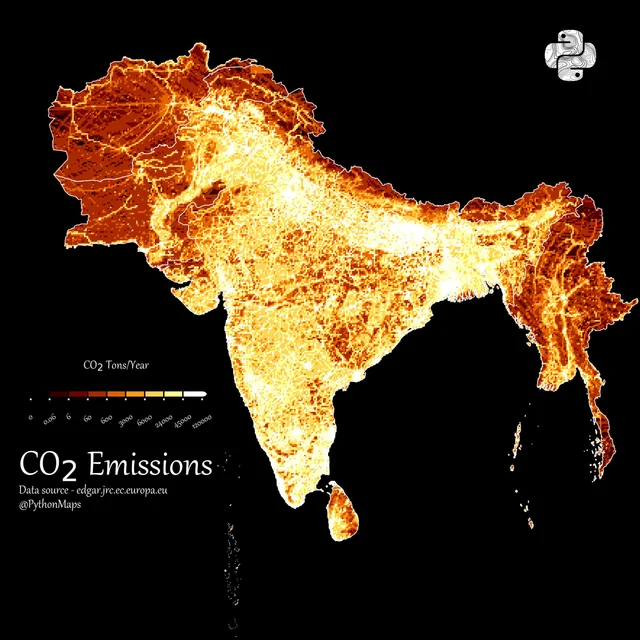







before people start making this about U.S and evangelism, i would like to ask is rule 1 enforced on comments?