No, the ancients did not “fail to see the colour blue”. Nor the Himba, mentioned in the text. Both simply don’t assign the shades that you’d call “blue” in English to their own special colour word. Each language splits the colour space in different ways.
I’ll illustrate this with an example in the opposite direction - English using a single primary word for colour, while another language (Russian) uses two:

In Russian, those three are considered separated colours; they aren’t a hue of each other, goluboj is not sinij or vice versa, just like neither is zeljonyj. In English however you’d lump the first two together as “blue”, and the third one as “green”.
Does that mean that your typical English speaker fails to see one of the first two shades? No. And if necessary they might even use expressions to specify one or another shade, like “sky blue” vs. “dark blue”. They still lump them together as “blue” though, unlike Russian speakers, and they might not pay too much attention to those silly details.
That’s basically what Himba speakers do, except towards all three of them. Here’s how the language splits colours:

You could approximate it in English as:
- vapa - white, light [anything]
- zoozu - black, dark but not reddish, purple
- serandu - more saturated reds and reddish oranges
- dumbu - more saturated yellows, yellowish oranges, and extra saturated greens
- burou - your run-of-the-mill green and blue
Now, check the colours that I posted with Russian terms. Just like English doesn’t care about the difference between two of them, Himba doesn’t care about the third one either.
There’s also an interesting case with Japanese, that recently split 青/ao and 緑/midori as their own colours. Not too much time ago, Japanese did the same as Himba, and referred to the colour of grass and the sky by 青/ao; however people started referring to the yellower hues of that range by 緑/midori (lit. “verdure”), until it became its own basic word.
That’s actually problematic for traffic legislation, because it requires the colour of traffic lights to be 青/ao, and people nowadays don’t associate it with green. Resulting into…

…cyan lights. They’re blue enough to fit the letter of the legislation, but green enough to be recognised as green lights!
Now, regarding specific excerpts from the text:
Gladstone noticed Homer described the sea color as “wine-dark,” not “deep blue,” sparking his inquiry.
Gladstone (and sadly, many people handling ancient texts) likely had the same poetic sensibility as a potato.
The relevant expression here is ⟨οἶνοψ πόντος⟩ oînops póntos; it’s roughly translatable as “wine-faced sea”, or “sea that looks like wine”. Here’s an example of that in Odyssey, Liber VII, 250-ish:
[245] ἔνθα μὲν Ἄτλαντος θυγάτηρ, δολόεσσα Καλυψὼ ναίει ἐυπλόκαμος, δεινὴ θεός: οὐδέ τις αὐτῇ μίσγεται οὔτε θεῶν οὔτε θνητῶν ἀνθρώπων. ἀλλ᾽ ἐμὲ τὸν δύστηνον ἐφέστιον ἤγαγε δαίμων οἶον, ἐπεί μοι νῆα θοὴν ἀργῆτι κεραυνῷ [250] Ζεὺς ἔλσας ἐκέασσε μέσῳ ἐνὶ **οἴνοπι πόντῳ**Murray translated that as “wine-dark”:
[245] Therein dwells the fair-tressed daughter of Atlas, guileful Calypso, a dread goddess, and with her no one either of gods or mortals hath aught to do; but me in my wretchedness did fate bring to her hearth alone, for Zeus had smitten my swift ship with his bright thunderbolt, [250] and had shattered it in the midst of the wine-dark sea.
Why would be Homer referring to the colour of the sea? It’s contextually irrelevant here. However, once you replace that “wine-dark” from the translation with “inebriating”, suddenly the expression makes sense, Homer is comparing the sea with booze! He’s saying that it’s dangerous to enjoy that sea, that you should be extra careful with it. (You could also say that the sea is itself drunk - violent and erratic).
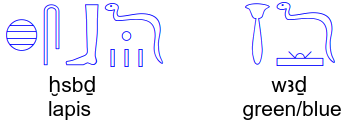
The ancient Egyptians were the first to adopt a word to describe the color blue.
I’m really unsure if this is the exception that proves the rule (since the Egyptians synthesised a blue dye from copper silicate) or simply incorrect.
At least accordingly to Wiktionary, the word ḫsbḏ* refers to lapis lazuli (the mineral) and its usage for colour is non-basic (a hue). The actual primary word for what English calls “blue” is shared with what English calls “green”, and it would be wꜣḏ*.
*in hieroglyphs:
Whatever the fuck podcast popularized the idea that blue just didn’t exist? Yeah stupid.
I do believe there is some relationship between one’s main language and how it affects thought patterns, but I mean cmon, even if I don’t know every word for shades of green (avocado VS chartreuse) doesn’t mean I’m not capable of distinguishing them. I may not have an exacting language tool set for distinguishing them. But I could.
Speaking of the relationship between language and thought patterns, chartreuse is clearly a red color.
Excellent post in general, but it should be noted that the meaning of “wine-dark sea” is still very much disputed.
Frankly, I think that the only reason why this is considered “disputed” is because a lot of pedants that gravitate towards classical texts are like Gladstone. They don’t see what the author says, on a discursive level; they see individual words, and that screws with their ability to understand metaphors, thus poetry, thus the epics.
For reference. I don’t speak Greek, but I do speak Latin. If I were to drink a sip of booze every bloody time that a muppet translated Plautus (a comedian) with unfunny shite, or Caesar (a general) with flowery and convoluted words, my liver would be probably floating the same seas as Odysseus’ ship. (It’s likely the same with Sanskrit given the egregiousness of “I am become Death”.)
This guy colours.
Thank you very much!
Thanks!
They didn’t have trouble recognizing blue. How would that even work? Blue things were and are blue. The article includes lots of bullshit which is to be expected for a site that has all kinds of pseudoscientific bullshit and pseudoarchaeology.
Its not about wavelength but about peoples ability to perceive and distinguish.
Blue is a rare pigment in nature so in most ancient cultures its often being categorized as a shade of green.
To give you an example of the opposite:
The Himba tribe of Namibia is known for their unique perception of color, particularly in how they differentiate shades of green. Research has shown that the Himba are more adept at distinguishing between various shades of green that many “civilized” might see as similar.
I don’t actually care about the linguistic side of it; we call a green traffic signal a blue light here in Japan (and the new ones are more blueish, but the old ones were much more green). I think Vietnamese and other languages do that.
When I skimmed the article, it was arguing that people literally could not see the blue, or at least was worded thusly where I looked before noping out of there. The literal title is “Hidden Hue: Why Ancient Civilizations Failed to See the Color Blue?” Not “failed to give it its own name” but “failed to see”.
Edit: punctuation.
Clickbait be clickbait and half the site is probably ai generated. I wont defend the hyperbole.
Theres is a debate you can have to what attributes to seeing in relation to perception. Our mind has a lot of tricks to get around the restrictions of our eyes.
Its a shame how enshitification erodes this conversation.
Yeah, there are definitely interesting conversations to be had. I actually saw an interesting video on the vision/linguistic side. I was just trying to find it to share but, speaking of enshitification, yoube’s search is ass. Why can’t I search in my subscriptions?!
I left that problem behind me a long time ago
Yt-dlp+jellyfin+invidious
I want to better understand this because the sky is clearly a specific color that has been there since the beginning.
How did proto humans not look up at the sky and considered in their feeble brains, “everything above the ground is this very unique color. It’s different from the ground, and the plants.”
I get that sea and lakes really don’t look blue. But did they look up and not see some shade of blue on a clear day?
My understanding is that they don’t distinguish blue and green as separate colours. Kind of like pink is just light red and not every language has a separate word for pink and red.
I’m here for this, I recently found out that I can’t really distinguish shades very well, so pink just looks mostly red and I have a really hard time telling blue from green, but can usually make it out if I look hard enough and get at least 2 guesses.
Either that or my wife got my doctor in on a really intense year long prank.
I think I have this same issue with red/pink and when a color is one or the other in that in-between area. I also do this with blue and green as well, though I feel less so than pink/red. I also have done colorblindness tests myself and do not test as colorblind (either variety).
For the longest time orange was just called yellow-red so it tracks.
Humans didn’t really care much about details until lately.
Iirc either Greek or Latin use the same word for hands as they do arms or something like that.
Orange being seen as shades of either red or yellow is also why they’re called redheads, it predates the word Orange entering the english language and being a better descriptor of most of the shades in that range of hair colors.
In modern Greek there’s still no distinction between arms and hands, or feet and legs.
Depending on where you are, water can definitely look very blue or even vivid green.
There’s been research that language shapes how we perceive the world around us. Because there was no word for “blue” there was no concept of blue, the color still existed but their brains just lumped it into “green”. Sight works by the visual centers brain taking data from the eyes, throwing most of it out, then building a model which is what the rest of the brain gets to actually “see”. That’s why optical illusions work.
A commonly cited source for language shaping our perception of color is Jules Davidoff’s studies on the Himba tribe. The Himba have no word for blue, and they struggled to pick out the blue square from this color wheel. However, they do have many distinctions for shades of green so when given this color wheel they could easily pick out the square that’s a different shade of green (and yes I opened it in MSpaint to check and one of the green squares is a different shade.)
It’s just terminology. People make a much bigger deal out of it than it is.
I think part of this phenomena is that the color of the sky on a clear day just wasn’t considered as a color, it was ‘blank’, the absence of clouds, stars or sunset. Kind of like how water has a flavor but we consider it to be neutral.
Homer referred to the ocean as “wine dark”, if you’ve seen pictures of the Mediterranean around Greece, that shit’s as Blue as Blue can be, so what it probably boiled down to is that they could “see” blue, but they always understood it as a blackish color or Green if they had distinguished that by that point.
Basically, there wasn’t a lot of necessity use in distinguishing blue, so most people didn’t until recently.
The idea that people not being able to describe/name the color blue means that they couldn’t see the color blue is the most unhinged takeaway from this.
cultures didn’t develop a name for a color until they were using that color as a dye, for the most part. Red usually comes first, and blue usually comes last, because red dye is usually really easy to make and blue is not. if you showed something cyan to somebody from like 500 years ago, and they told you that it was just blue, you wouldn’t assume that they couldn’t see the color cyan. they just didn’t have a word for it cuz they didn’t need one (I don’t actually know how old cyan is but you know what I mean).
to this day there are still some languages that consider blue to be a shade of green. in Russia, light blue is concerted a separate color from blue just like pink is considered separate from red; in the Iliad, Homer compares the color of the sky to bronze, maybe referring to the blue-green patina that forms on it. he referred to the ocean as “wine-dark”.
color naming is weird.
Dyes play a huge role, but it boils down to relevance.
Dark vs. light is probably the first thing that becomes relevant for us, as the difference is [literally] like night and day; then hot colours (red, etc.) because of fruits and blood. Then the rest.
I didn’t dig too much into Homer’s usage of “bronze sky” (unlike the wine-faced = inebriating sea), but if I had to take a guess, he wasn’t referring to the colour but calling it “glorious”, or perhaps a “noble” sky.
yeah, in other contexts when he’s using the word, like when describing people, he’s referring to bronze’s intrinsic properties. he might have also been referring to the color of sky at sunset
Article reads like it was written by an LLM that watched too much TV
Lapis Lazuli was traded along the Silk Road, and Homer would have called it Sapphirus. A stormy sea isn’t blue because it’s not reflecting a blue sky, and it may have roiled-up sand and kelp.
Isn’t it the most recent major color?
Every language initially embraced words for black and white, symbolizing darkness and light, followed by red, associated with blood and wine. Subsequently, yellow and green entered linguistic lexicons, with blue consistently lagging behind as the last hue universally recognized.
It was also the most illusive color to create with LED. It’s why blue lights on devices are so popular, because it’s new.
Asianometry is a great channel
Was it not orange?
Blue is the new orange












