I didn’t say anything about Kant himself (Kant also thought that non-human animals were basically just “things” without rationality or self-consciousness, which is however in direct conflict with the current scientific consensus. Kant still argued in favour of treating animals “humanely”, just not for their own sake). Anyway, some well-known and well-respected contemporary philosophers who argue(d) from a Kantian perspective in favour of animal rights include e.g. Christine Korsgaard or Tom Regan, and many lesser known philosophers (see e.g. here for a recent example). I also see no indication that these types of arguments as a whole are supposedly “thoroughly rebutted” (not that serious philosophy really works like that anyway). Some other philosophers disagree with some of their arguments, of course (this is normal in philosophy), and many don’t subscribe to Kantianism in the first place, but afaik most of them tend to take issue with how Kantian ethics is applied (or that it is applied) moreso than that they’re trying to defend animal exploitation as such. Either way, none of that changes the fact that ethicists have been using Kantian ethics (among many other meta-ethical frameworks, as I said before) to argue in favour of animal rights, and that there aren’t really many arguments in defense of killing animals for food (in particular in the context of factory farming) that find widespread support (among moral philosophers, that is).
- 0 Posts
- 24 Comments
I didn’t think the had an official organized statement
There sort of is. The term “vegan” was coined by some members of the Vegetarian Society of the UK in the 1940s (at the time veganism and vegan diet were mostly referred to by terms such as “strict vegetarianism” or “no animal food” etc.), who shortly after founded the Vegan Society [of the UK]. The latter has an “official” definition of veganism:
Of course individual vegans may have slightly different definitions, and may interpret them differently, but as a whole this seems to be a fairly accurate definition for many vegans (although there are some exceptions, e.g. people who adopt plant-based diets for (percieved or actual) health benefits, or religious reasons, sometimes (but not always) also refer to themselves as “vegans”).
As to the “literally right” part (I assume the OP was referring to veganism in general, not the specific issue of the thread), it mostly boils down to whether or not we think the statement “it is (morally) wrong to unnecessarily cause harm to animals” is correct. Since most people (with perhaps the exception of some with rare medical conditions) can survive just fine on a diet free of animal products (same goes for clothing etc.), we can conclude that it is at least unnecessary to use animal products. Thus, if we agree with the rest of the statement (i.e. that exploiting animals for their meat or other products causes them harm) we should also agree with veganism as an ethical stance. Naturally this could be discussed in much more detail and with many caveats, but for me this is more or less the core of the argument. And as it turns out, a lot of moral philosophers from different meta-ethical schools (such as utilitarianism, Kantian ethics or virtue ethics) seem to agree at the very least that the arguments in favour of veganism are much stronger than those in defense of eating meat (and particularly those in defense of factory farming). Some further reading for those interested:

 9·10 months ago
9·10 months agoThere seems to be a bit of a difference, even though both involve asking questions. To quote wiktionary:
sealioning (uncountable)
A type of trolling or harassment that consists of pursuing people with relentless requests for evidence, often tangential or previously addressed, while maintaining a pretense of civility and sincerity (“I’m just trying to have a debate”), and feigning ignorance of the subject matter, in order to wear down an opponent and incite angry responses that will discredit them.Apparently coined by this webcomic:
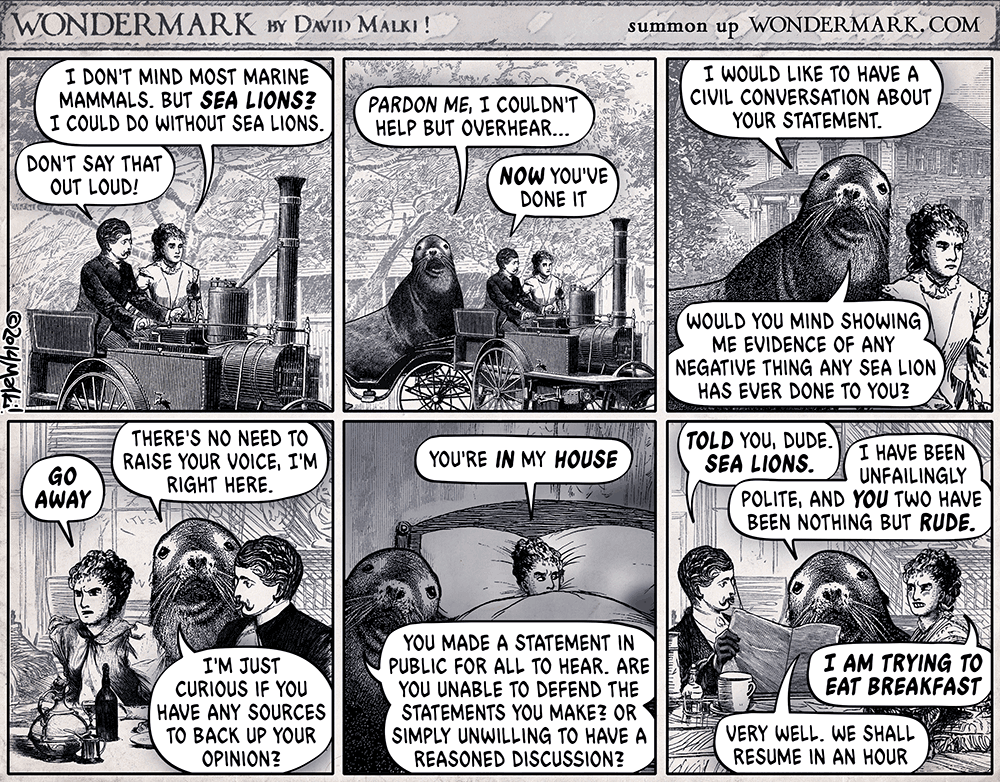
JAQ off (third-person singular simple present JAQs off, present participle JAQing off, simple past and past participle JAQed off) (slang, derogatory) To ask loaded questions inviting someone to justify their views or behaviours, in an attempt to make tangential claims of little verisimilitude appear acceptable.
So the way I understand it, “JAQing off” is when you’re trying to guide your audience towards a certain conclusion without stating it outright (e.g. “Are the official numbers of holocaust victims really as solid as people claim? Are there alternative historical interpretations? I’m just asking questions here, not implying anything folks.” when you think just saying “The holocaust didn’t happen!” might make it too obvious you’re a Nazi), while sealioning is more about annoying the other party and trying to make them look bad/unreasonable and yourself polite and reasonable in comparison (e.g. “I’m just curious, is there any actual evidence that fascists are inherently bad people, as you claim? As a person with no opinion on the matter, I would just like to have an honest and open debate on this subject.” so when people reply with something like “Fuck off, fascist!” you can say “Wow, so much for the tolerant left.”). Both tactics are frequently applied by online trolls, especially of the far right, but they have somewhat different goals.

 311·1 year ago
311·1 year agoIt’s precisely what everyone said would happen.
I don’t disagree with your general point, but I remember that there were many people (on reddit, but also on lemmy) who said there would be lots of power-hungry redditors just waiting to take over and that the admins would thus have no trouble at all finding replacements.
That takes something from being completely unreasonable to be understandable.
Why would taxing a gross income of above a billion US$ by ~66% be “completely unreasonable”? Imo taxes for such incomes should generally be higher if anything.
It seems you’re misunderstanding the map. It’s how much space each of those categories is taking up as a fraction of the total area of the contiguous US, not where that land use primarily occurs.
Streets aren’t really mentioned either, besides “Rural highways”. I assume other streets and parking spaces are mostly included in “Urban/Rural housing” and/or “Urban commercial” (smaller rural streets might not be counted seperately from the surrounding land).
As a non colorblind person, I would like to understand how this image could have been modified to include our colorblind brethren.
In general it is a good idea to use colour gradients that monotonically increase (or decrease) in brightness in addition to (or instead of) hue (see here for an in-depth comparison of different colour maps. It’s from a Python package, but it shows some interesting plots comparing different colour maps when it comes to brightness vs. hue). This isn’t just useful for colour blind people, but also helpful when printing in black-and-white.
If you absolutely have to use a diverging colour map, you might reach most people by using blue as a major component of one, but only one of the two branches (the map in the OP uses blue as a major component of both branches, which is why red/green colour blind people can have a problem with it). That way most colour blind people should be able to distinguish the branches, since blue colour blindness (Tritanopia/Tritanomaly) is much rarer than red (Protanopia/Protanomaly) or green (Deuteranopia/Deuteranomaly) colour blindness.
Apart from that it is also possible to mark information visually in other ways than by colour, e.g. by shapes and patterns, like dotted or dashed lines for line graphs, shaded or dotted areas for bar and area graphs, or different geometric shapes like crosses, diamonds, and circles when plotting individual data points, but that is probably more useful when different sets of data are plotted in the same graph.
In what world is a country with billionaires and an autocratic ruling class in which the workers decidedly do not control the means of production, “socialist”?

 13·1 year ago
13·1 year agoA similar recent article that I thought was interesting and contains many sources: https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/23778399/media-ignores-climate-change-beef-meat-dairy. It focuses a bit more on the role of media though. They also have this older article on big meat lobbying.

 31·1 year ago
31·1 year agoIt’s from a longer quote in “A Brief, Incomplete and Mostly Wrong History of Programming Languages” about the language Haskell:
1990 - A committee formed by Simon Peyton-Jones, Paul Hudak, Philip Wadler, Ashton Kutcher, and People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals creates Haskell, a pure, non-strict, functional language. Haskell gets some resistance due to the complexity of using monads to control side effects. Wadler tries to appease critics by explaining that “a monad is a monoid in the category of endofunctors, what’s the problem?”
Some other languages like e.g. Rust also use monads. The point I was trying to make humorously was that many programming languages sometimes do use math concepts, sometimes even very abstract maths (like monads), and while it’s not maths per se, programming and computer science in general can have quite a bit to do with maths sometimes.

 71·1 year ago
71·1 year agoThe article gives another reason:
Authorities say the river will help expand agricultural land and reduce the need to import food and wheat.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine in February last year drove a global surge in wheat prices, leaving Egypt struggling as it is the world’s biggest wheat importer.In addition, in recent years there have been droughts in East Africa as well, which can’t have been good for the amount of water the Nile carries, and the dam you mention just adds to the whole thing.

 22·1 year ago
22·1 year agoFor those wondering like me where the water is supposed to come from:
Authorities have said that water for the artificial river will come from recycled agricultural drainage and groundwater.
This doesn’t really strike me as a long term solution though, unless Egypt has vast reserves of groundwater.

 73·1 year ago
73·1 year agocoding has nothing to do with math
A monad is just a monoid in the category of endofunctors, what’s the problem?
lesser function
Putting aside that this might be difficult to quantify, why do you think it matters? There are some groups of humans who exhibit severely diminished mental capacities compared to the average human (e.g. babies, severely mentally handicapped people, people in a coma, etc.). Would it be okay to eat them? Because I’m fairly confident that for whatever measure to compare cognitive functions you could come up with, we would be able to find at least some humans who perform worse on them than the average pig, for example.
different species
Why does this matter? As a hypothetical thought experiment, do you think it would be morally justified for us to eat aliens who are biologically very different from us but of comparative intelligence (or higher)? Or for them to eat us?
it’s the easiest, most accessible, most fulfilling, and healthiest way
Apart from the “fulfilling”, which is arguably subjective, I don’t think the rest is true. At least I don’t see how not eating meat would be difficult or “inaccessible” in a significant way, and considering the last point studies regularly show that vegetarians and vegans are, on average, slightly healthier than other people if anything (which might be in part just correlation, but it does contradict your claim of meat being the “healthiest” way to get nutrients).
Fuck Tyson though, those bastards can go to hell.
On this we can definitely agree.
they are not sentient
Science disagrees with you here. Most of the animals being used for meat are in fact not just sentient, but also conscious:
Convergent evidence indicates that non-human animals have the neuroanatomical, neurochemical, and neurophysiological substrates of conscious states along with the capacity to exhibit intentional behaviors. Consequently, the weight of evidence indicates that humans are not unique in possessing the neurological substrates that generate consciousness. Non-human animals, including all mammals and birds, and many other creatures, including octopuses, also possess these neurological substrates.
– From the Cambridge Declaration on Consciousness
nature intended
Nature doesn’t intend anything, it simply is. We are, in the grand scheme of things, not separate from nature, and in this sense everything we do is natural. If you’re using “natural” to distinguish things from the results of human civilization, then eating animal products stemming from animal agriculture is just as “unnatural” as supplements, as both are products of civilization.


The author of the article you mentioned (Alex Howe) is a good example for what I insinuated: He takes issue with Korsgaard’s argument (and, it seems, Kantian ethics more generally), but in his PhD thesis argues for granting “basic citizenship rights” to domestic animals (including farm animals), which is arguably a far more radical position than veganism, which merely posits that it is immoral to exploit (or be cruel towards) animals (e.g. as a food resource). Either way, if you have an issue with Kantian ethics and how they are applied to animal rights, I suggest you take it up with a Kantian (which I am not). And, even if I am repeating myself, none of this has any direct relevance to my earlier point, which is that many moral philosophers from many different schools of thought (including, but by no means limited to, Kantian ethics) have arrived at conclusions which are at least similar to the basic vegan stance, i.e. that unnecessarily causing harm to (sentient) animals, e.g. by exploiting them as food, is immoral.